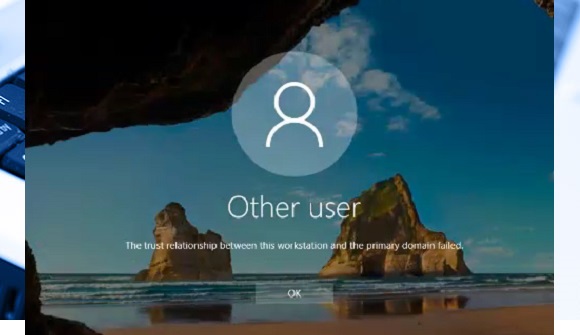
Windows: The trust relationship between this workstation and the primary domain has failed
29 April 2022Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!
When you log on to a computer that is running domain-joined Windows, and you receive the message “error The trust relationship between this workstation and the primary domain has failed”.
What causes the error “The trust relationship between this workstation and the primary domain has failed”
This error indicates that this computer is no longer trusted. The local computer password does not match the object password for this computer stored in the AD database.
Explanations
When you join the computer to the Active Directory domain, the new computer account is created for your device and a password is set for it (similar to AD users).
The trust relationship at this level is provided by the fact that the domain join is performed by a domain administrator. Or another user with delegated administrative permissions performed the join.
Each time the domain computer logs into the AD domain, it establishes a secure channel with the nearest domain controller (%logonserver% environment variable). DC sends computer credentials. In this case, trust is established between the workstation and the domain. Further interaction occurs according to the security policies defined by the administrator.
The computer account password is valid for 30 days (default) and then changes. You must keep in mind that the computer changes the password according to the configured domain group policy. It is like a process of changing a user’s password.
You can configure the maximum account password age for computers in the domain using the GPO setting Domain Member: Maximum Computer Account Password Age.
It is located in the following section of the Group Policy Editor: Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > Security Options
You can specify the number of days between 0 and 999 (by default it is 30 days).
The Active Directory domain stores the computer’s current password, as well as the previous one. If the password has been changed twice, the computer using the old password will not be able to authenticate to the domain controller. This will not establish a secure connection channel.
Computer account passwords do not expire in Active Directory. This happens because the domain password policy does not apply to AD Computer objects. Your computer can use the NETLOGON service to change the password the next time you log in to the domain. This is possible if his password is more than 30 days old. Note that the local computer’s password is not managed by AD, but by the computer itself.
The computer tries to change its password on the domain controller. Only after a successful change does he update his local password. A local copy of the password is stored in the registry key HKLM\SECURITY\Policy\Secrets$machine.ACC
Password Last Set
You can view the time of the last password set for a computer object account in the AD domain using the PowerShell cmdlet
1 | get-adcomputer -Identity LT230 -Properties PasswordLastSet |
How to solve the problem
To solve this problem there are several methods:
Method 1
The most popular, which is to remove the computer from the domain, then rejoin the computer to the domain.
- Right-click Computer > Properties .
- Select Change settings next to the computer name.
- On the Computer Name tab , select Change .
- Under the Member of heading , select Workgroup , type the name of a workgroup, and then select OK .
- When prompted to restart the computer, select OK .
- On the Computer Name tab , select Change again .
- Under the Member of heading , select Domain , then type the name of the domain.
- Select OK , and then type the credentials of the user with permissions in the domain.
- When prompted to restart the computer, select OK .
- Restart the computer.
Method2
The Reset-ComputerMachinePassword PowerShell cmdlet changes the password for the account that computers use to authenticate to domain controllers.
- Log in with a local administrator account
- Launch PowerShell as administrator
- Enter the following command:
1 | Reset-ComputerMachinePassword -Server "nom-du_DC" -Credential Compte_admin_du_domaine@chader.fr |
- Restart the computer.
- The Reset-ComputerMachinePassword PowerShell cmdlet is not available in PowerShell Core 6.0 and 7.x due to the use of unsupported APIs.
Method3
Via the Netdom utility , it can be installed on the client’s PC with the RSAT (Remote Server Administration Tools) package. To use it, login to the target system with local administrator credentials, open the cmd.exe prompt as administrator and run the following command
1 | Netdom resetpwd /Server:nom_du_DC /UserD: Compte_admin_du_domaine /PasswordD:mot_de_pass |
- Restart the computer.
Method4
You can verify that the computer’s local password is synchronized with the computer account password on the domain control.
To do this:
- Log in to the computer under the local administrator account
- Start the PowerShell console
- Run the Test-ComputerSecureChannel cmdlet.
1 | Test-ComputerSecureChannel |
you can add the –Verbose switch parameter:
1 | Test-ComputerSecureChannel -Verbose |
You can repair a secure channel between the computer and the Active Directory domain start the PowerShell console and run the following cmdlet:
1 | Test-ComputerSecureChannel -Repair -Credential Compte_admin_du_domaine@chader.fr |
- Enter Password
- Restart the computer.
Views: 1991




